Major merchants welcome AI agents, Amazon blocks competition
Research shows UK/US retailers embrace agentic commerce opportunities while Amazon remains notable exception, implementing bot restrictions.
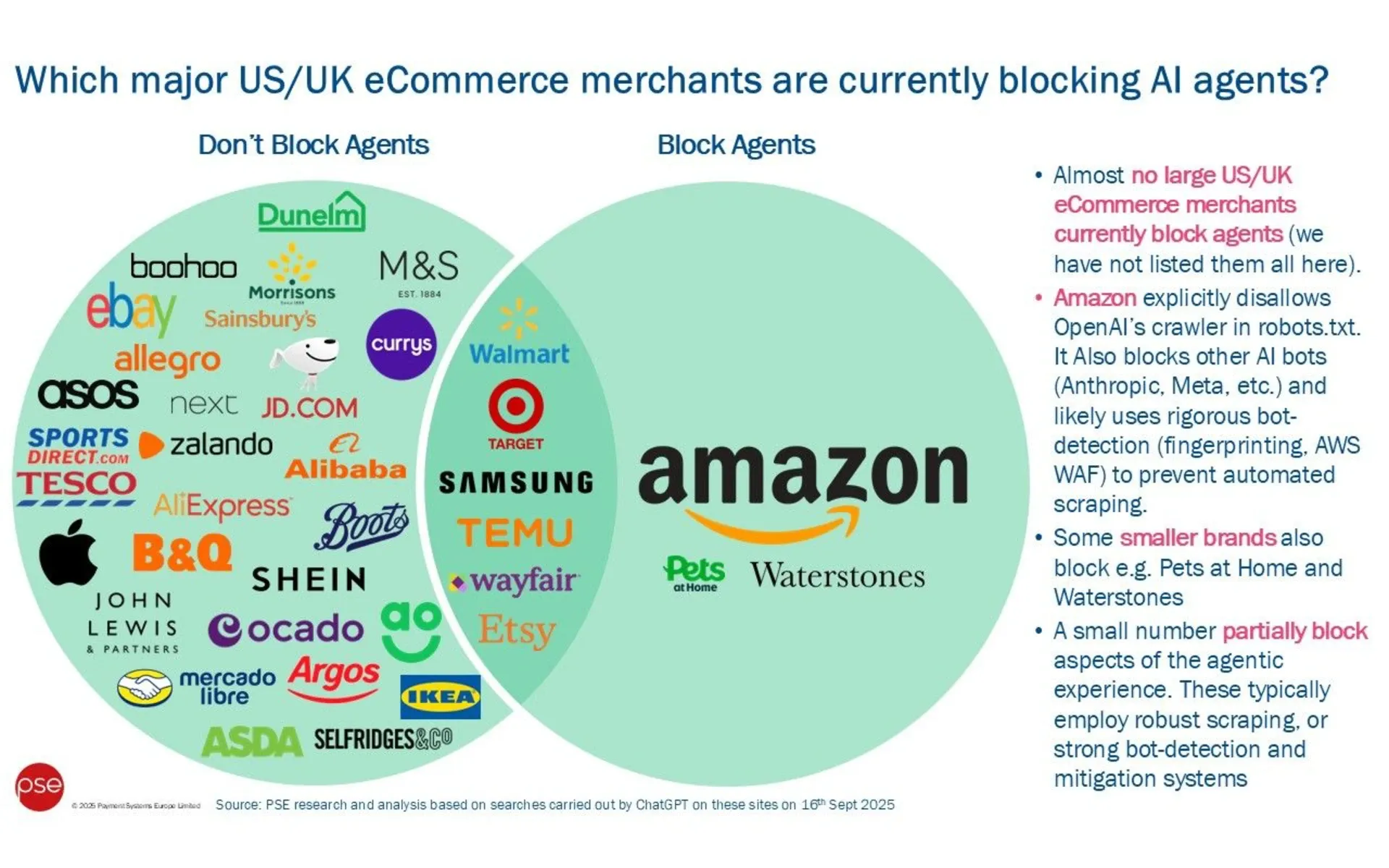
Chris Jones, Managing Director at PSE Consulting, published findings on September 16, 2025, revealing that major UK and US eCommerce merchants actively welcome artificial intelligence agents rather than blocking them. The research contradicts widespread assumptions about merchant resistance to agentic commerce, with Amazon standing as the primary exception implementing comprehensive bot restrictions.
According to Jones' analysis, "almost all the merchants we speak to are very keen to engage with the new agentic environment and, on the whole, welcome the opportunities presented to attract and engage new customer groups." The consulting firm specializes in payments and fintech, working with clients across the European market for over 20 years.
The findings challenge prevailing industry narratives about merchant hostility toward AI shopping agents. Jones characterized blocking agents as "generally regarded as too extreme: using a hammer to crack a nut." Most retailers view agentic commerce as an opportunity rather than a threat to their existing customer relationships.
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Technical implementation varies across merchants
The PSE Consulting review examined top UK and US eCommerce sites, analyzing their technical approaches to AI agent detection and management. The research identified distinct categories of merchant responses to artificial intelligence crawlers and automated shopping systems.
Merchants expressing enthusiasm for AI agents prioritize identification and monitoring over outright blocking. "Their concerns focus mainly on being able to identify and monitor the activities of agents so they can understand how they differ from traditional direct to consumer modes of shopping," Jones explained. This approach treats AI agents as a new customer segment requiring specialized management strategies.
The identification process enables merchants to develop tailored optimization approaches. Once AI agents are detected, retailers begin "the process of managing them like any other customer group: understanding what drives conversion, how to manage messaging, exceptions, risk etc." This methodology mirrors traditional customer segmentation practices adapted for autonomous shopping systems.
However, several major platforms maintain active bot detection systems that may interfere with agentic experiences. Companies including Temu and Wayfair employ "active bot blocking which may impact the agentic experience," according to the research. These restrictions stem from "genuine concerns about bots, rather than agentic commerce itself."
Amazon maintains restrictive policies
Amazon represents the most significant exception to merchant openness toward AI agents. The retailer explicitly disallows OpenAI's crawler in robots.txt and blocks other AI bots from Anthropic, Meta, and similar companies. The platform uses "rigorous bot-detection" including fingerprinting and AWS WAF to prevent automated scraping.
The restrictions align with Amazon's development of competing AI shopping tools. The company launched Rufus, an AI chatbot currently testing advertising features, alongside a "buy-for-me" feature that purchases items from third-party websites for customers. These internal developments position Amazon to control AI integration on its platform while restricting external agent access.
Industry analysts view Amazon's blocking strategy through competitive lenses. Eric Seufert from Mobile Dev Memo argued that blocking AI agents serves Amazon's business interests. "The fundamental flaw with 'agentic commerce' or 'agentic advertising' is that it violates the motivations of retail outlets to control the customer relationship and monetize their first-party data with advertising," Seufert observed.
Industry implications for agentic commerce
The research reveals broader implications for the emerging agentic commerce landscape. Most retailers recognize the potential value of AI-mediated shopping experiences while maintaining control over customer interactions. This balanced approach contrasts sharply with Amazon's restrictive policies.
Smaller retailers may benefit from embracing AI agents while larger platforms maintain restrictions. Advertising technology expert Karsten Weide suggested that "blocking personal shopping bots will be a losing defensive battle," predicting competitive advantages for specialized retailers that welcome agentic commerce.
The shift toward AI-mediated commerce could reshape advertising strategies across the industry. Weide indicated that "D/R advertising will fade. Brand advertising will gain in importance as we want to influence consumers before they tell their agent what to do." This transformation would prioritize brand awareness campaigns over direct response formats currently dominating digital marketing.
Technical considerations for AI agent management
The PSE Consulting findings highlight technical requirements for effective AI agent integration. Merchants require robust identification systems capable of distinguishing between malicious bots and legitimate AI shopping agents. This distinction determines whether automated systems receive restricted access or full commerce functionality.
Successful AI agent management involves multiple technical components. Merchants must implement tracking systems that monitor agent behavior patterns, conversion rates, and interaction methods. These analytics enable optimization of AI-specific user experiences while maintaining security against harmful automated activities.
The identification process also enables specialized customer journey optimization. AI agents may exhibit different browsing patterns, product selection criteria, and purchasing behaviors compared to human shoppers. Understanding these differences allows merchants to tailor interfaces, product recommendations, and checkout processes for optimal agent performance.
Competitive dynamics in AI commerce
The divergent approaches between Amazon and other major retailers reflect broader competitive dynamics in AI-powered commerce. Amazon's restrictions protect its data advantages while potentially limiting customer choice in AI-mediated shopping experiences.
Competing platforms including Shopify have adopted different strategies. Shopify introduced warning language to merchants' robots.txt files rather than implementing comprehensive blocking. The platform's "Robot & agent policy" requires "buy-for-me" agents to include human review steps and integrate Shopify's checkout technology.
Walmart and eBay have not implemented changes blocking AI bots from their sites, according to reviews of their robots.txt files. This divergence suggests different strategic approaches to balancing competitive positioning with potential benefits from AI-powered shopping tools.
Buy ads on PPC Land. PPC Land has standard and native ad formats via major DSPs and ad platforms like Google Ads. Via an auction CPM, you can reach industry professionals.
Market research supports merchant optimism
The PSE Consulting findings align with broader market research indicating growing acceptance of AI commerce tools. Recent analysis suggests that 80% of companies utilizing cybersecurity firm HUMAN Security's platform chose to block known large language model user-agents outright, but this primarily reflects security concerns rather than opposition to legitimate agentic commerce.
The marketing community has shown increasing interest in AI agent integration opportunities. Amazon's introduction of agentic AI across its seller platform demonstrates internal recognition of AI agent value while maintaining external restrictions.
The development of specialized AI commerce tools continues accelerating across the industry. Technical guides for building functional AI marketing agents have emerged from developer communities, addressing implementation challenges for organizations seeking autonomous marketing systems.
Future implications for retail marketing
The research suggests fundamental changes approaching the retail marketing landscape. As merchants develop AI agent management capabilities, traditional customer acquisition and retention strategies may require significant adaptation.
Marketing professionals must consider how products appear to algorithmic recommendation systems rather than solely human shoppers. Success will likely require optimization of product data, specifications, and metadata to ensure visibility when customers make natural language requests to AI assistants.
The direct integration of AI agents into commerce platforms raises questions about customer journey ownership and attribution. Marketing teams accustomed to direct customer relationships may need to recalibrate acquisition strategies, lifetime value calculations, and performance measurement frameworks.
Data from the research indicates that merchants view AI agents as complementary to existing customer channels rather than replacement systems. This perspective enables development of integrated strategies that leverage both human and AI-mediated shopping experiences for optimal business outcomes.
The findings position most major retailers for proactive engagement with agentic commerce while Amazon maintains its restrictive approach. This divergence creates distinct competitive dynamics that may influence customer behavior and platform selection as AI shopping agents become more prevalent.
According to Jones, "Amazon is the merchant exception, not the rule" in approaches to AI agent management. This assessment suggests the broader retail industry recognizes opportunities in agentic commerce while the largest platform maintains protective barriers against external AI integration.
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Timeline
- September 16, 2025: Chris Jones publishes PSE Consulting research showing major UK/US merchants welcome AI agents despite assumptions
- September 17, 2025: Amazon introduces agentic AI across seller platform while blocking external AI bots
- August 29, 2025: Amazon blocks AI bots from major tech companies amid commerce battle
- July 21, 2025: Agentic AI threatens traditional DSP business models according to industry analysis
- July 27, 2025: McKinsey identifies AI agents reshaping advertising landscape in technology outlook
- June 16, 2025: PayPal debuts shoppable storefront ads addressing agentic commerce rise
- April 21, 2025: Microsoft and OpenAI position for retail AI battle with shopping integrations
- September 2024: Technical guide emerges for building AI marketing agents addressing development challenges
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Summary
Who: Chris Jones, Managing Director at PSE Consulting, conducted research examining major UK and US eCommerce merchants' approaches to AI agents. The consulting firm specializes in payments and fintech with over 20 years of European market experience.
What: Research revealing that most major eCommerce merchants actively welcome AI agents and agentic commerce opportunities, contrary to widespread industry assumptions about merchant resistance. Amazon stands as the notable exception implementing comprehensive bot blocking measures.
When: Findings published September 16, 2025, based on PSE Consulting's review of top UK/US eCommerce sites and direct merchant conversations about AI agent integration strategies.
Where: Analysis covered major UK and US eCommerce platforms, with particular focus on technical implementation approaches across different merchant categories and platform policies toward AI agent access.
Why: The research addresses misconceptions about merchant hostility toward agentic commerce while highlighting competitive dynamics between platforms that welcome AI agents versus those implementing restrictive blocking measures. The findings matter for marketing professionals navigating the shift toward AI-mediated shopping experiences and planning strategies for emerging autonomous commerce channels.

