Interaction to Next Paint (INP) to replace First Input Delay (FID) on March 12, 2024
In a significant move for web developers and user experience optimization, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) is set to become a Core Web Vital, replacing First Input Delay (FID) on March 12, 2024.
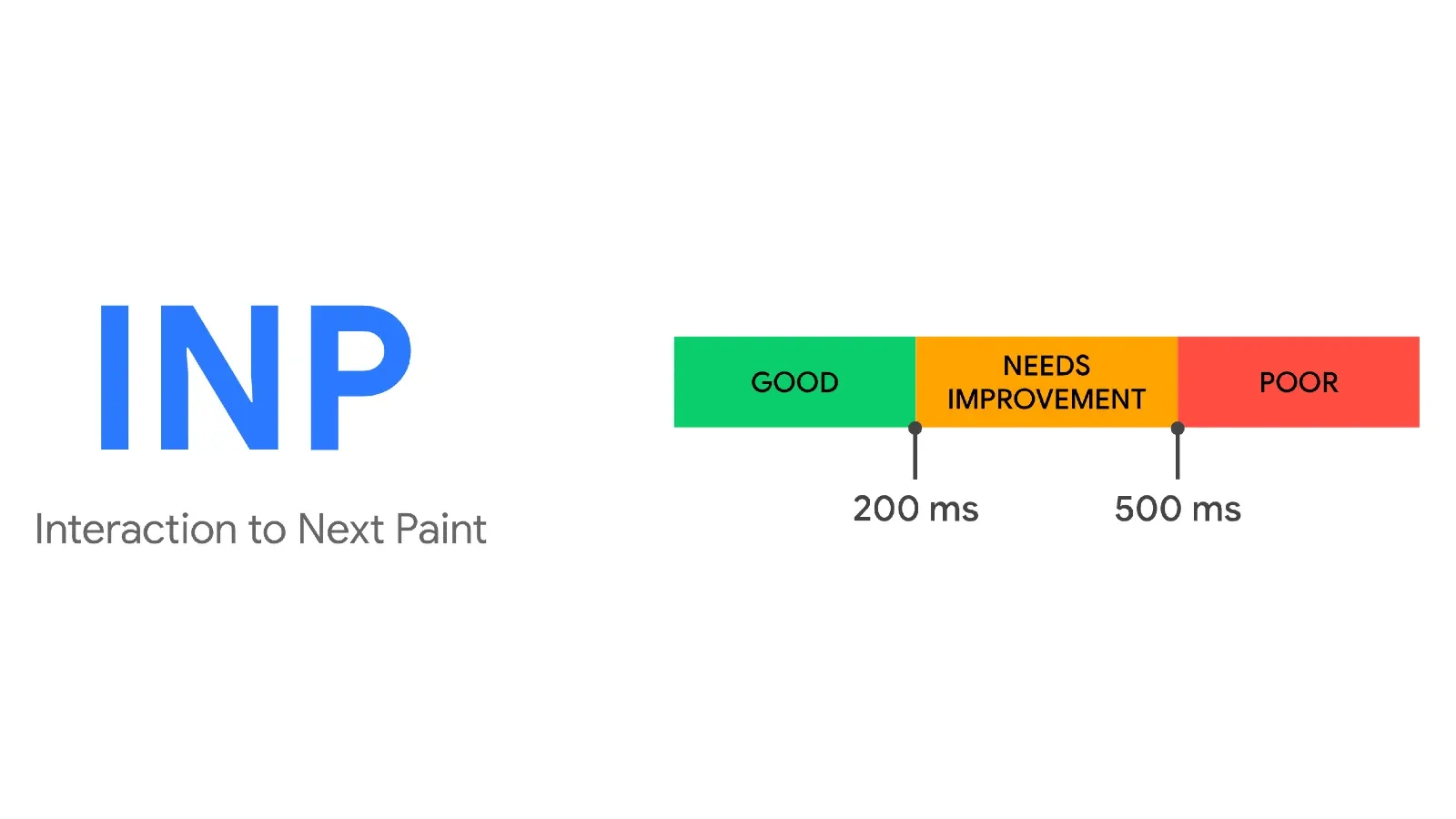
In a significant move for web developers and user experience optimization, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) is set to become a Core Web Vital, replacing First Input Delay (FID) on March 12, 2024.
The announcement comes after a careful two-year planning process by the Chrome team, highlighting the importance of capturing aspects of interactivity that FID did not fully address.
The Web Vitals program, which provides essential metrics for web developers, introduced INP as an experimental metric in May 2022. Over time, it evolved into a pending metric, and as of March 12, it will achieve stable status as a Core Web Vital, taking the place of FID.
Developers are encouraged to prepare for this transition by assessing their website's INP performance. The Chrome team suggests using tools like PageSpeed Insights, which utilizes the Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX), or Real User Monitoring (RUM) providers to gather field data. However, it's crucial to ensure that your website meets the eligibility criteria for inclusion in CrUX.
If INP is found to be in the "needs improvement" or "poor" category, resources are provided to help developers diagnose and troubleshoot issues. Guides cover topics such as optimizing long tasks, reducing input delay, handling large DOMs efficiently, and addressing complex CSS selectors.
The complexity of INP necessitates a multi-faceted approach to optimization. Several case studies, including those from The Economic Times and redBus, showcase how reducing interaction latency can positively impact business outcomes.
According to Google, once INP officially becomes a Core Web Vital, FID will be deprecated, and changes will be reflected in documentation across Google's tools. FID will be removed from Google Search Console immediately upon INP's Core Web Vital status, while other tools like PageSpeed Insights and CrUX will provide a six-month deprecation period for developers to update their code accordingly.
INP's inclusion in Core Web Vitals is seen as a significant step forward in assessing and improving the responsiveness of web pages comprehensively. The Chrome team believes that this holistic approach will lead to a more responsive web over time.

