German regulators challenge Amazon marketplace pricing policies
German competition authority objects to platform's algorithmic price caps affecting 60% of online retail.
The Bundeskartellamt delivered a preliminary assessment on June 2, 2025 - exactly today - finding Amazon's price control mechanisms likely violate German competition law. According to the authority, the e-commerce giant's Fair Pricing Policy restricts marketplace sellers through non-transparent algorithmic price caps that could constitute abuse under Section 19a(2) of the German Competition Act and Article 102 TFEU.
Get the PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for more like this
Amazon operates the amazon.de platform, which accounts for approximately 60 percent of online retail sales in Germany. The company uses this infrastructure both for its own Amazon Retail business and the amazon.de Marketplace, where third-party sellers offer products directly to consumers. This dual role creates inherent competition issues, according to regulators.
Amazon employs sophisticated algorithmic systems to monitor and control seller pricing across its platform. According to the Bundeskartellamt, the company "uses various algorithms and statistical models, drawing on different prices and price components of current or previous offers on Amazon, as well as those of external competitors, in order to calculate dynamic, changing price caps for the sellers' offers."
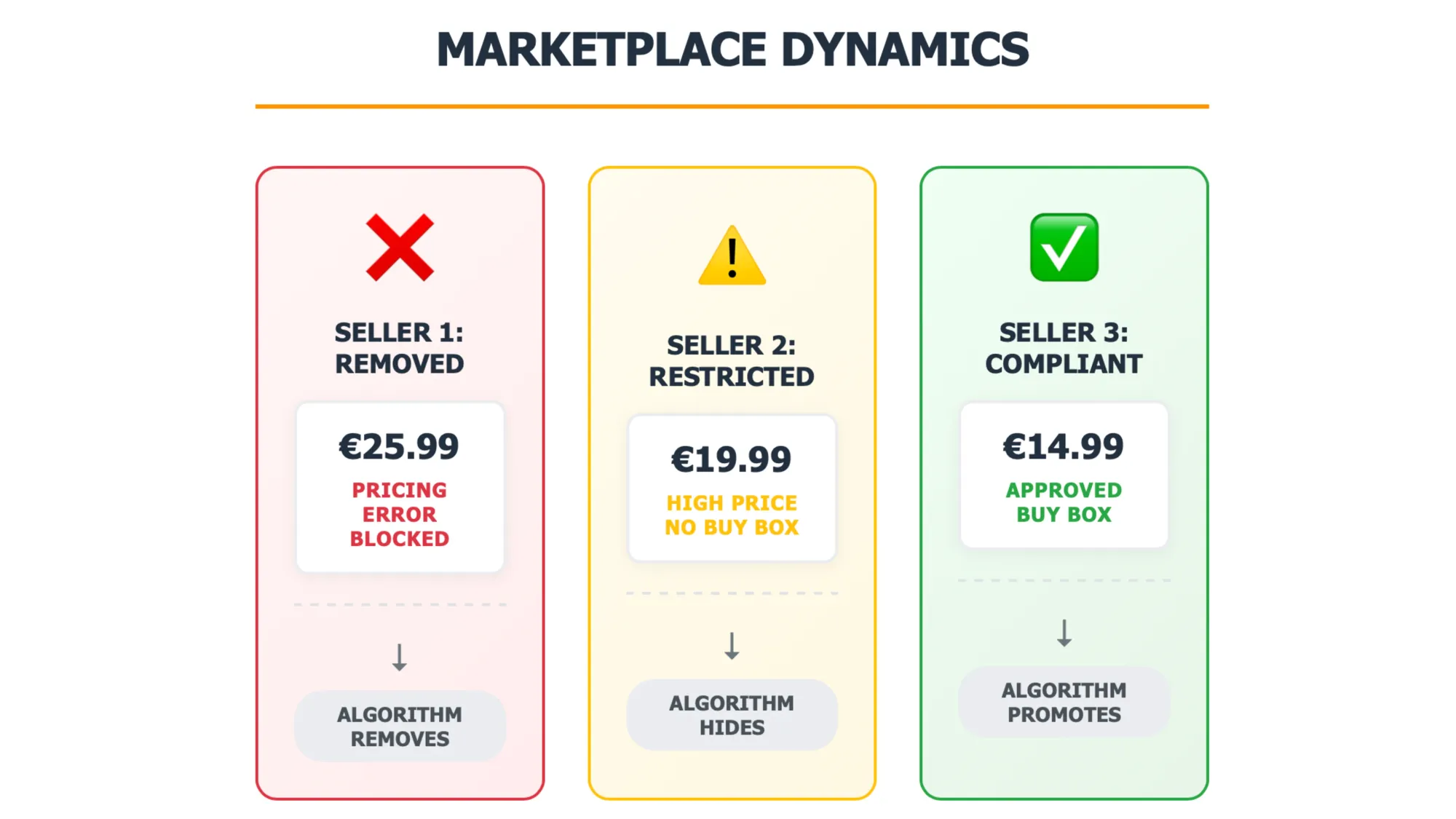
The system categorizes seller offerings into three distinct classifications. Products deemed "pricing errors" face complete removal from the marketplace. Those classified as "significantly high prices" or "uncompetitive prices" experience exclusion from the Buy Box feature, restricted display in search results, and potential exclusion from Amazon advertising programs.
When sellers exceed Amazon's algorithmic price thresholds, their product visibility diminishes significantly. According to the preliminary assessment, "It is possible that the Buy Box is not displayed at all for a certain product because none of the sellers comply with Amazon's price caps." Affected sellers receive notifications requesting price adjustments to Amazon's predetermined reference levels.
Competition concerns identified
Andreas Mundt, President of the Bundeskartellamt, stated: "Competition in Germany's online retail trade is largely determined by the rules Amazon sets for its trading platform. As Amazon directly competes with the Marketplace sellers on its platform, influencing its competitors' pricing, including in the form of price caps, is inherently problematic from a competition perspective."
The authority identified three primary areas of concern regarding Amazon's pricing mechanisms. First, the frequent modification of price caps without transparent criteria may restrict competitive processes on the marketplace. The assessment found these restrictions lack "objective, verifiable principles" and insufficient transparency in Amazon's communications with third-party sellers.
Second, the price control systems interfere with sellers' pricing freedom, potentially creating concentration effects on the marketplace. According to the preliminary findings, "strict price caps often mean that sellers are unable to cover their costs, putting them at risk of having to leave the Marketplace."
Third, Amazon's dual role as both platform operator and marketplace competitor enables coordination of marketplace prices according to its own pricing principles. The assessment particularly highlighted Amazon's practice of "systematically matching the lowest price found in other online shops across its entire trading platform" as potentially creating "a significant barrier to switching and deter other online retailers from engaging in price competition."
Legal framework and precedent
The investigation operates under Section 19a of the German Competition Act, which establishes special provisions for large digital companies. In July 2022, the Bundeskartellamt determined Amazon possessed "paramount significance for competition across markets," subjecting it to extended abuse control. The Federal Court of Justice confirmed this decision in April 2024.
Following this determination, the authority initiated proceedings under Section 19a(2) GWB in November 2022. According to the Bundeskartellamt, the preliminary assessment "is based on in-depth investigations, including a large-scale survey of online sellers" conducted in September 2024.
The Bundeskartellamt coordinates its approach with the European Commission, responsible for enforcing the Digital Markets Act, and the Bundesnetzagentur, which handles Platform-to-Business Regulation enforcement.
Methodology behind algorithmic pricing
Amazon's Fair Pricing Policy requires regular reviews of seller prices through automated systems. The company's algorithms incorporate multiple data sources, including current and historical pricing from both Amazon and external competitors. These systems generate dynamic price caps that change based on market conditions and competitive intelligence.
The mechanisms operate continuously, evaluating seller prices against calculated thresholds. When violations occur, the system implements immediate restrictions on product visibility and marketplace participation. According to the assessment, these automated decisions lack sufficient transparency, with "parameters of the price control mechanisms used by Amazon are set at its own discretion."
Market impact analysis
Germany's online retail market concentration around Amazon creates significant leverage for the platform's pricing policies. With amazon.de capturing approximately 60 percent of online retail sales, seller compliance with pricing requirements becomes essential for market access.
The preliminary assessment suggests Amazon's pricing coordination may create uniform pricing strategies across the platform "at the expense of other online sellers." This standardization potentially reduces price competition and innovation in online retail markets.
Mundt emphasized the broader implications: "This is particularly the case when the sellers in question are no longer able to cover their own costs and the trading platform is being used to hinder the rest of the online retail trade in a way that is contrary to competition law."
International context
This German investigation parallels similar regulatory scrutiny globally. The European Commission accepted binding commitments from Amazon in December 2022 covering French, German, and Spanish markets following concerns about third-party seller data usage and Buy Box preferences.
The UK Competition and Markets Authority secured binding commitments from Amazon in November 2023 addressing similar marketplace practices. Italy's competition authority previously imposed a €1.3 billion fine in December 2021 over allegedly unfair practices favoring Amazon's fulfillment services.
In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission filed proceedings against Amazon in September 2023, with an amended complaint in March 2024 alleging the company punishes sellers offering lower prices on competing platforms.
Technical enforcement mechanisms
Amazon's pricing surveillance operates through real-time monitoring of marketplace activities. The system processes vast amounts of pricing data, applying machine learning models to identify pricing anomalies and competitive positioning. When sellers attempt to set prices above algorithmic thresholds, automated responses immediately restrict product visibility.
The Buy Box feature represents a critical component of Amazon's pricing enforcement. Products excluded from Buy Box display experience dramatic reductions in sales potential, effectively compelling seller compliance with pricing requirements. According to the assessment, this mechanism provides Amazon substantial control over marketplace competition dynamics.
Why this matters
This regulatory action signals increasing scrutiny of algorithmic pricing controls across digital platforms. Marketing professionals operating marketplace strategies must navigate evolving compliance requirements while maintaining competitive positioning.
The case demonstrates how platform policies directly impact seller profitability and market access. Brands relying heavily on Amazon for distribution face growing regulatory uncertainty around pricing freedom and platform dependency.
Additionally, the investigation highlights the tension between platform optimization and competition law. Marketing teams must balance algorithm compliance with independent pricing strategies to maintain regulatory compliance and competitive positioning.
Timeline
July 2022: Bundeskartellamt determines Amazon has paramount significance for competition, subjecting it to extended abuse control under Section 19a GWB. Federal Court of Justice confirms this decision in April 2024.
November 2022: Bundeskartellamt initiates proceedings under Section 19a(2) GWB investigating Amazon's marketplace practices.
September 2024: Authority conducts large-scale survey of online sellers as part of investigation.
January 2025: UK Competition Appeal Tribunal selects Prof Andreas Stephan's collective proceedings application against Amazon, representing over 200,000 UK-based merchants in case covering alleged anti-competitive practices from 2015-2024. Related story
June 2, 2025: Bundeskartellamt issues preliminary assessment finding Amazon's price control mechanisms likely violate German and European competition law. Amazon receives opportunity to respond to allegations.

