Chrome browser enhances form autofill to reduce checkout abandonment rates
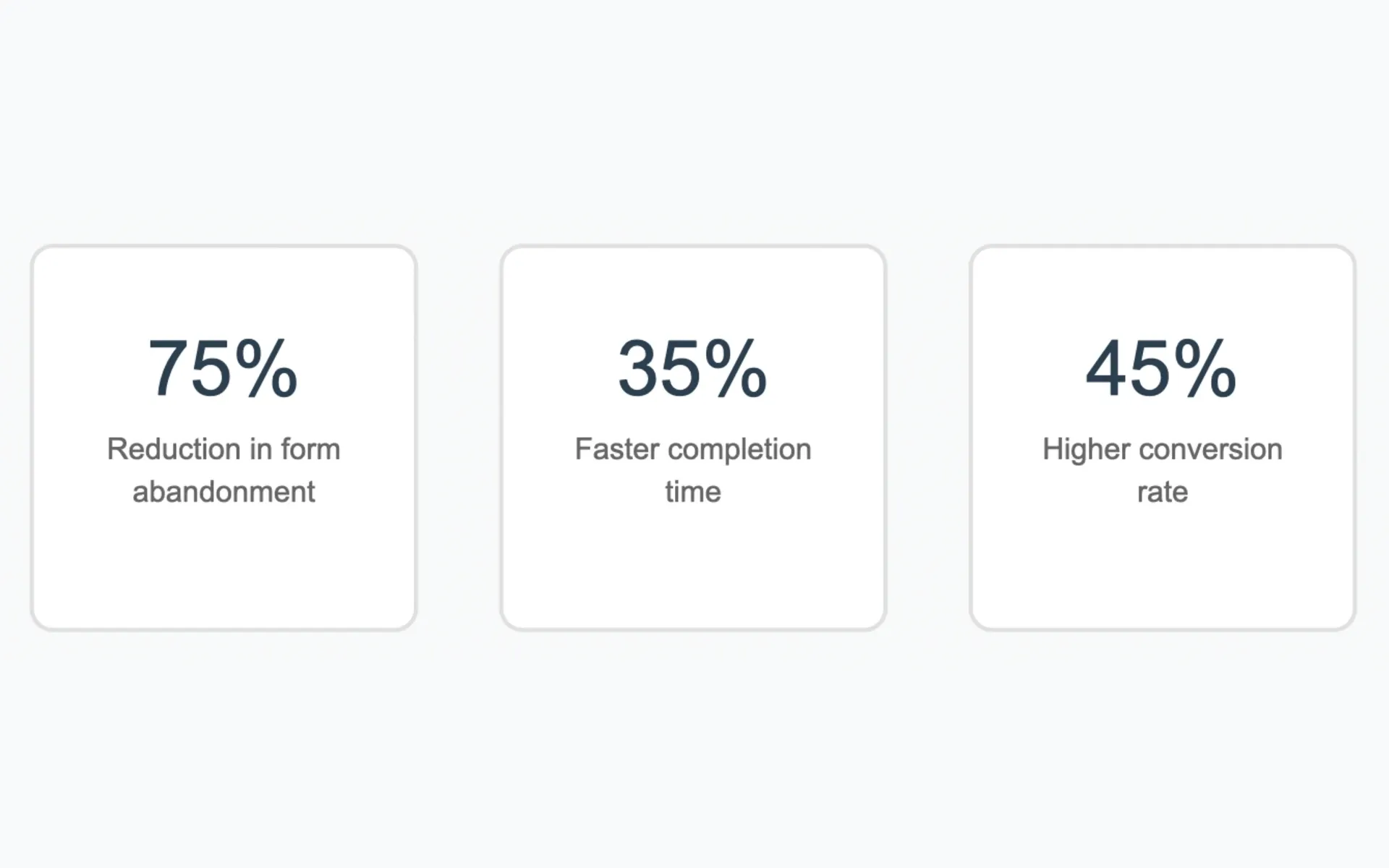
Google's Chrome team releases autofill improvements showing 75% reduction in form abandonment and 35% faster completion times.
Six days ago, on December 20, 2024, Google Chrome's Product Strategy Lead Lokesh Khurana announced significant improvements to the browser's autofill capabilities. According to internal research conducted by the Chrome team, the enhanced autofill functionality demonstrates measurable impacts on online shopping behaviors.
The research, which analyzed data from thousands of the most visited websites in Chrome across the United States, revealed substantial improvements in form completion metrics. According to the Chrome team's analysis of aggregated contact and payment forms data from consenting users, websites implementing the autofill feature experienced a 75% reduction in form abandonment rates.
The technical implementation allows Chrome to automatically populate website form fields with previously saved information across devices. The system encompasses various data types, including contact details, passwords, and payment information. The browser's security architecture maintains data protection while enabling cross-device synchronization for users signed into their Google accounts.
Shopify, which manages commerce operations for more than 10% of U.S. ecommerce transactions and serves 644 million customers across 175 countries, reported specific performance metrics. The platform's internal testing revealed that guest checkouts utilizing autofill demonstrated a 45% higher Checkout Conversion Rate (CCR) compared to non-autofill sessions.
The technical architecture includes country-specific address field support and enhanced field detection capabilities. The system processes address fields in multiple languages, adapting to regional variations in address formats and field structures. This localization approach aims to accommodate diverse global commerce requirements.
The measured impact on user interaction times showed a 35% reduction in form completion duration. The Chrome team's analysis suggests this improvement stems from the elimination of manual data entry and reduced typing errors during the checkout process.
Security measures implemented in the system include fingerprint and device lock verification options. Users must provide initial security code verification for payment methods, with subsequent transactions allowing biometric authentication. The architecture maintains separate security settings at the device level, requiring individual configuration for each device.
The system's payment processing framework interfaces with Google Pay integration, though users maintain control over payment information storage preferences. The implementation allows users to manage security codes separately, with options to enable or disable automatic security code population during transactions.
The browser's form detection capabilities extend beyond standard checkout forms to include various data entry scenarios. The system can identify and populate address fields, payment details, and contact information across different website implementations.
Chrome's data management architecture allows users to control their stored information through the browser's settings interface. The system provides options for adding, editing, or removing saved data, with changes synchronizing across devices for signed-in users.
The technical infrastructure includes verification mechanisms to ensure secure data transmission. Websites must meet specific security requirements to access the autofill functionality, with Chrome implementing checks to verify site security before enabling data population.
Google's research methodology involved analyzing aggregated data from consenting users, focusing on form completion patterns across major websites. The findings suggest correlations between autofill usage and successful transaction completion, though multiple factors contribute to checkout success rates.
The implementation continues to evolve, with the Chrome team developing additional features and expanding language support. These developments aim to address varied global commerce requirements while maintaining security and user control over data management.

