AI researcher challenges claims of development slowdown with exponential data
Julian Schrittwieser presents METR and OpenAI evaluation data showing models completing 2-hour tasks, contradicting bubble theories as GPT-5 approaches human expert performance.
Julian Schrittwieser, a Member of Technical Staff at Anthropic and former Principal Research Engineer at DeepMind, published a comprehensive analysis on September 27, 2025, directly addressing widespread claims about AI progress stagnation. The researcher, known for his work on groundbreaking algorithms including AlphaGo, AlphaZero, and MuZero, presented data from multiple evaluation frameworks showing continued exponential improvement in AI capabilities.
According to Schrittwieser's analysis, recent discourse around a supposed AI "bubble" mirrors early reactions to COVID-19 pandemic exponential growth patterns. "Long after the timing and scale of the coming global pandemic was obvious from extrapolating the exponential trends, politicians, journalists and most public commentators kept treating it as a remote possibility or a localized phenomenon," he wrote on his blog.
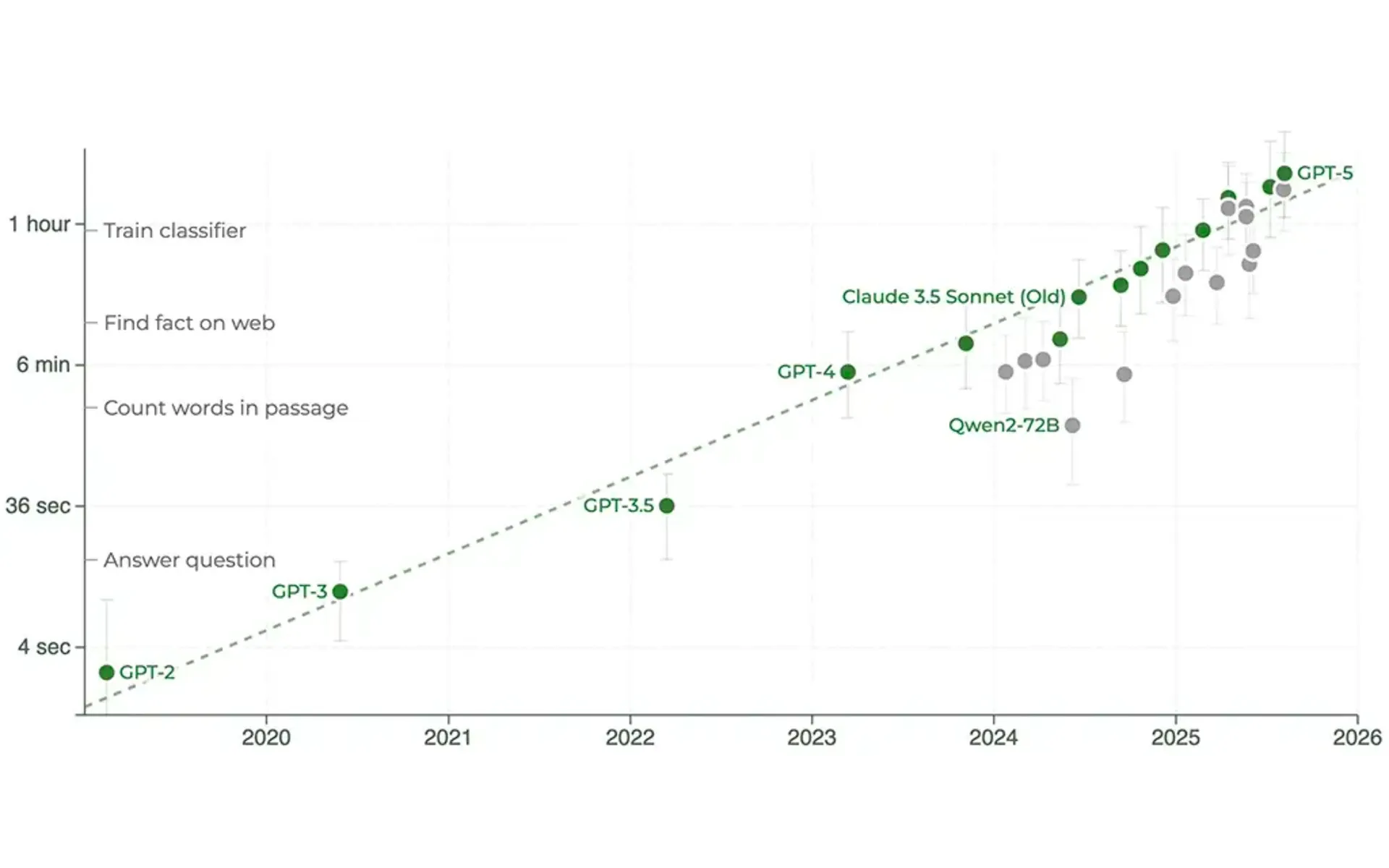
The analysis centers on two major evaluation studies. METR (Model Evaluation & Threat Research) published findings showing AI systems can now autonomously complete software engineering tasks lasting up to two hours at 50% success rates. Their data demonstrates task length capabilities doubling every seven months, with models like Grok 4, Opus 4.1, and GPT-5 exceeding predicted performance trajectories.
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
OpenAI's GDPval evaluation, measuring performance across 44 occupations spanning nine industries, supports these findings. The comprehensive study analyzed 1,320 tasks created by industry professionals averaging 14 years of experience. Grading utilized blinded comparison methodology between human and model-generated solutions.
GPT-5 achieved remarkable proximity to human performance levels across multiple sectors. However, Claude Opus 4.1 demonstrated superior capabilities, matching industry expert performance in many evaluated tasks. "I want to especially commend OpenAI here for releasing an eval that shows a model from another lab outperforming their own model - this is a good sign of integrity and caring about beneficial AI outcomes," Schrittwieser noted.
The METR evaluation tracked progression from GPT-2's 1-second task completion capability in 2020 to current models handling multi-hour autonomous work. Sonnet 3.7, despite being seven months old, achieved 50% success rates on one-hour tasks. Recent additions including Grok 4, Opus 4.1, and GPT-5 demonstrated capabilities extending beyond two hours.
Software engineering represents just one domain showing exponential advancement. The GDPval study encompassed diverse sectors including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and professional services. Tasks ranged from real estate management to medical administration, legal analysis, and technical engineering challenges.
Industry professionals created evaluation criteria based on realistic workplace scenarios. Each occupation contributed 30 tasks, ensuring comprehensive coverage of professional requirements. The methodology addressed potential bias concerns by utilizing experienced practitioners rather than academic test creators.
Performance variations among recent models revealed important insights. Both Grok 4 and Gemini 2.5 Pro underperformed relative to benchmark scores claimed during release announcements. This pattern highlights evaluation methodology differences and the importance of standardized assessment frameworks.
Schrittwieser's projections, based on consistent exponential trends, suggest significant milestones approaching rapidly. Models may achieve autonomous work capabilities spanning full eight-hour workdays by mid-2026. At least one system could match human expert performance across multiple industries before 2026 ends.
By 2027, models may frequently surpass expert-level performance on numerous tasks. These predictions rely on extrapolating established trend lines rather than speculative breakthrough assumptions.
The analysis addresses common misconceptions about AI development cycles. Many observers focus on conversational differences between consecutive model releases, missing underlying capability improvements measurable through structured evaluations. Surface-level interactions provide incomplete pictures of technical advancement.
PPC Land has extensively covered AI's marketing implications, particularly regarding autonomous systems reshaping advertising operations. McKinsey's analysis identified agentic AI as the most significant emerging trend for marketing organizations, attracting $124.3 billion in investment during 2024.
Marketing technology platforms continue integrating AI capabilities through intelligent agents automating complex workflows. Adverity's September 12, 2025 launch demonstrated conversational AI enabling direct data interaction while automated agents handle specialized tasks like marketing mix modeling.
The evaluation methodologies address real-world application concerns. METR's tasks include debugging, feature implementation, and system troubleshooting scenarios. GDPval encompasses client consultation, regulatory compliance, and strategic planning challenges across industries.
Professional services showed particular advancement potential. Legal analysis, financial planning, and management consulting tasks demonstrated strong model performance improvements. Healthcare administration and technical engineering also showed significant capability gains.
Manufacturing and retail sectors displayed steady progress in AI-assisted operations. Supply chain optimization, inventory management, and customer service tasks showed measurable improvement trajectories. These sectors represent substantial economic impact potential as capabilities scale.
Buy ads on PPC Land. PPC Land has standard and native ad formats via major DSPs and ad platforms like Google Ads. Via an auction CPM, you can reach industry professionals.
Schrittwieser emphasized the importance of understanding exponential growth patterns. Mathematical extrapolation often provides more accurate predictions than expert intuition in rapidly changing technical domains. Historical examples include internet adoption, mobile technology deployment, and computing power advancement.
The research connects to broader industry developments around AI infrastructure demands. Europe faces significant challenges meeting AI energy requirements, with the Netherlands experiencing unprecedented grid congestion as data centers require electricity equivalent to 100,000 households each.
Evaluation limitations require acknowledgment. METR tasks average approximately 3 on a 16-point messiness scale, where regular software engineering work typically rates 7-8. Real-world applications often involve coordination, ambiguous requirements, and organizational constraints not captured in controlled evaluations.
GDPval tasks similarly focus on well-defined, digital-only scenarios with complete instruction sets. Many professional responsibilities involve proprietary software, colleague communication, and iterative refinement cycles extending beyond evaluation scope.
Despite these limitations, both evaluation frameworks provide valuable benchmarking for AI capability assessment. They establish measurable progress metrics while acknowledging the complexity of real-world application scenarios.
The analysis reinforces growing recognition of AI's transformative potential across industries. Marketing professionals report increased traffic from AI implementations rather than the predicted devastation, with 55.5% observing growth since AI Overviews introduction.
However, accuracy concerns persist in AI-generated marketing guidance, with WordStream research finding 20% error rates across major platforms. Google AI Overviews showed 26% incorrect responses while Google Gemini achieved only 6% errors.
Technical infrastructure development continues addressing scalability challenges. Companies implement sophisticated AI agent frameworks for marketing automation, with Adobe's Experience Platform Agent Orchestrator and Amazon's marketplace management systems leading enterprise adoption.
Schrittwieser's background lends credibility to his analysis. His contributions to reinforcement learning include co-inventing human feedback techniques and leading development of transformer architectures. Previous roles at Google Brain and OpenAI provided direct experience with large-scale AI development.
The researcher's publication timing coincides with increased industry scrutiny of AI progress claims. Investment patterns, deployment challenges, and performance variations across applications create complex assessment environments requiring careful analysis.
Professional evaluators like METR provide essential third-party assessment capabilities. Their specialized focus on AI capability measurement offers objective frameworks for tracking development progress beyond marketing claims or anecdotal observations.
OpenAI's transparency in releasing comparative evaluation data demonstrates industry maturation toward standardized assessment practices. Cross-laboratory evaluation creates accountability mechanisms supporting accurate progress reporting.
The exponential growth patterns documented across multiple evaluation frameworks suggest continued rapid advancement despite surface-level plateauing perceptions. Mathematical trend analysis provides systematic approaches for understanding complex technological development cycles.
Future evaluation methodologies will likely address current limitations through expanded task complexity, longer evaluation periods, and integration with real-world deployment scenarios. These improvements will enhance prediction accuracy while maintaining objective assessment standards.
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Timeline
- 2020: GPT-2 achieves 1-second task completion capability according to METR evaluation framework
- 2022-2024: Consistent doubling of AI task completion lengths every seven months established through METR tracking
- May 2024: Google breaks publishers' business models with new AI search experiment
- July 2024: 80% of companies block AI language models, HUMAN Security reports
- July 10, 2025: One in five AI responses for PPC strategy contain inaccuracies, study finds
- July 13, 2025: Dutch grid crisis exposes Europe's AI energy infrastructure gap
- July 21, 2025: Technical guide emerges for building functional AI marketing agents
- July 26, 2025: Marketing concerns over AI search may be overblown, study finds
- July 27, 2025: McKinsey: AI agents reshape advertising landscape
- August 5, 2025: Meltwater debuts GenAI Lens for comprehensive brand monitoring across AI platforms
- August 19, 2025: Investor claims AI apps generate hundreds of Google queries per request
- September 12, 2025: Adverity debuts AI-powered intelligence layer for marketing analytics
- September 27, 2025: Julian Schrittwieser publishes "Failing to Understand the Exponential, Again" analyzing METR and GDPval data
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Summary
Who: Julian Schrittwieser, Member of Technical Staff at Anthropic and former Principal Research Engineer at DeepMind, known for contributions to AlphaGo, AlphaZero, MuZero, and other breakthrough AI algorithms.
What: Comprehensive analysis challenging AI progress stagnation claims using METR and OpenAI GDPval evaluation data showing continued exponential capability improvements, with models now completing 2-hour autonomous tasks and GPT-5/Claude Opus 4.1 approaching human expert performance levels.
When: Published September 27, 2025, addressing current industry discourse about supposed AI development plateaus and bubble theories gaining prominence throughout 2025.
Where: Analysis published on Schrittwieser's personal blog, drawing from METR evaluation data covering software engineering tasks and OpenAI's GDPval study spanning 44 occupations across 9 industries globally.
Why: Addresses widespread misconceptions about AI progress by presenting objective evaluation data showing consistent exponential improvement trends, countering surface-level observations and anecdotal claims about development slowdowns that could impact investment, policy, and strategic planning decisions.

